Identification of cytokine profiles in blood samples from kidney transplant recipients
Ariunaa Altangerel1, Gansukh Chojilsuren1, Ulziikhuu Tumurkhuyag1, Enkhtushig Gavaabaljir1, Sarantsetseg Jigjidsuren3, Tsogtsaikhan Sandag1, Khongorzul Togoo1,2.
1Department of Immunology, Mongolian National University of Medical Sciences, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia; 2Institute of Biomedical sciences, Mongolian National University of Medical Sciences, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia; 3Department of Clinical laboratory, The First Central Hospital of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
Background: Cytokines, pivotal in the immune response following organ transplantation, serve as vital indicators of inflammation and guide immunosuppressive therapy. Precise cytokine analysis facilitates inflammation monitoring and immunosuppressive drug optimization kidney transplant recipients.
Objective: This study aimed to delineate the cytokine profiles of kidney transplant patients pre and post transplantation utilizing flow cytometry.
Materials and Methods: Conducted from July 2023 to March 2024, the study encompassed 10 kidney transplant recipients (5 male, 5 female; mean age 36±12.01 years) at the National University of Medical Sciences. Blood samples were collected before transplantation and at 7 and 30 days post surgery. Utilizing the Human Inflammation Panel 2, a 13-cytokine analysis was performed simultaneously employing the TC 13-plex (BioLegend®) bead-based multiplex assay panel, employing fluorescence-encoded beads suitable for flow cytometry. Statistical analyzes employed analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Results: Evaluation of 13 cytokines (TGF-β1, PAI-1, sTREM-1, PTX3, sCD40L, sCD25, CXCL12, sST2, sTNF-RI, sTNF-RII, sRAGE, CXCL1, sCD130) revealed notable variations pre and post transplantation. Specifically, TGF-β1, sCD40L, sTNF-RII, and sRAGE exhibited elevated levels pre transplantation, which significantly decreased post transplantation (p<0.05). Conversely, the levels of other cytokines remained statistically unchanged pre and post transplantation (p>0.05). (Table 1)
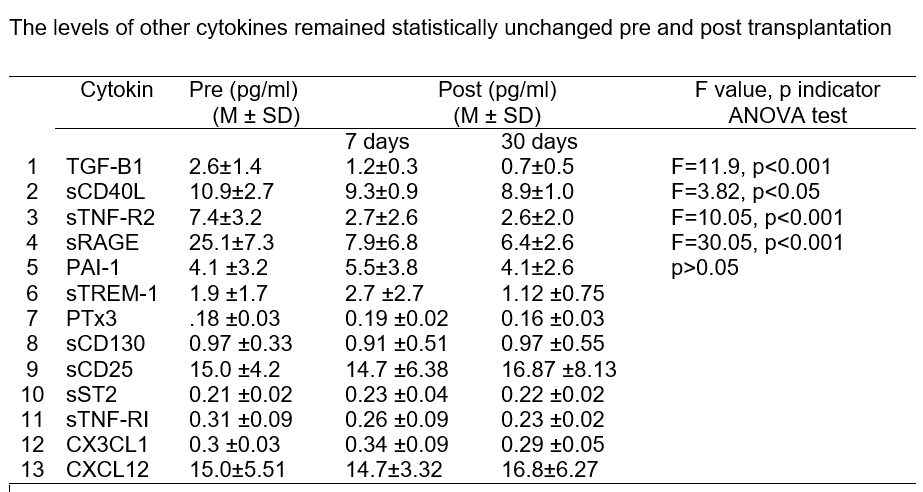
Conclusion: The study highlights a significant decrease (p<0.05) in TGF-β1, sCD40L, sTNF-RII, and sRAGE cytokine levels at 7 and 30 days post kidney transplantation, underscoring their potential as biomarkers for monitoring post transplant inflammatory responses.
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the following institutions for their support and collaboration throughout this study: Department of Immunology, Mongolian National University of Medical Sciences Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Mongolian National University of Medical Sciences Department of Clinical Laboratory, The First Central Hospital of Mongolia We extend our appreciation to the faculty, staff, and researchers at these institutions for their valuable contributions to this research project. Additionally, we thank the kidney transplant recipients who participated in this study for their cooperation and willingness to contribute to medical research..
