Longitudinal SARS-CoV-2 antibody and T-cell immune responses in vaccinated kidney transplant recipients and patients on dialysis
Renato Foresto1,2, Pedro Oliveira2, Monica Rika Nakamura1,2, Roberto Matias Souza1, Haryanne Goulart1,2, Rayra Sampaio2, Daniela França2, Helio Tedesco-Silva1,2, Lúcio Requião-Moura1,2, José Medina-Pestana1,2.
1Nephrology Division , Universidade Federal de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil; 2Hospital do Rim , Fundação Oswaldo Ramos, São Paulo, Brazil
Introduction: Kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) have an inferior immune response to vaccination due to chronic immunosuppression compared to dialysis patients (DPs). This study aims to measure the effect of de novo immunosuppression on long-term humoral and cellular immune response in CKD patients submitted to kidney transplant.
Methods: This is a prospective interventional study comparing the post-vaccination humoral and cellular response in de novo KTRs and DPs. All patients received at least two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine, and none had previous disease. Blood samples were collected on inclusion, and after 1-, 3-, 6- and 12 months and tested for anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG, neutralization antibody activity, and IFN-ɣ activity. The primary outcome was sororreversion at month 12. Patients with anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG negative at inclusion were excluded. All patients received additional doses of COVID-19 vaccine during this study, according to the governmental recommendations.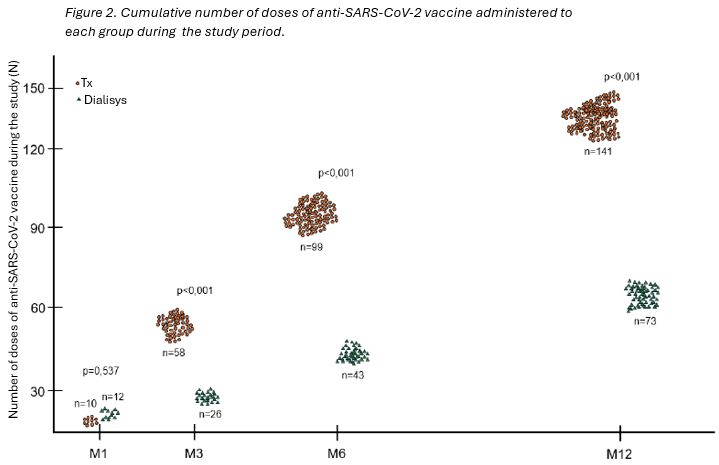
Results: There was no sororreversion during the period of follow-up. The anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG titers were similar at Screening, 1, 3 and 12 months and lower in KTRs at 6 months [KTR 5,529.8 (IQR 2,514.2-19,337.4); DP 14,427.9 (IQR 6,605.5-35,285.2); p<0.001).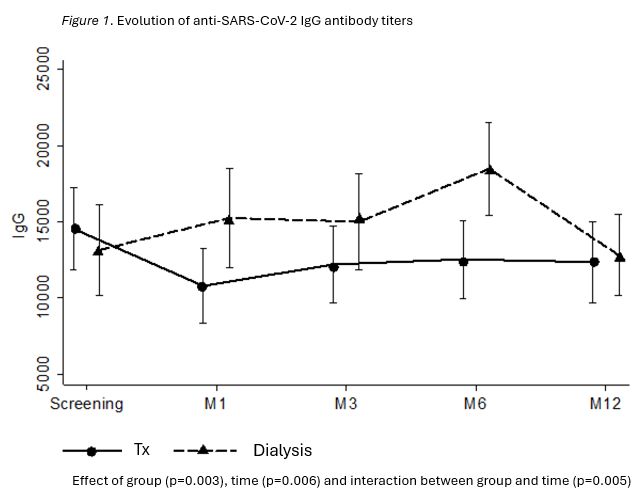 The neutralizing antibody activity was high and similar at all study visits (p=0.938). The IFN-ɣ activity was lower in KTRs at screening (7.1% vs. 24.7%; p<0.001) and similar between the groups during the follow-up. After the first month, the cell-T immune response decreased within each group until month 6: KTR (M1 19.6%; M3 11.0%; M6 4.1%; p<0.001) and DP (M1 22.1%; M3 6.8%; M6 2.2%; p<0.001) but increased in both groups at month 12 (KTR 17,9%; DP 13,7%).
The neutralizing antibody activity was high and similar at all study visits (p=0.938). The IFN-ɣ activity was lower in KTRs at screening (7.1% vs. 24.7%; p<0.001) and similar between the groups during the follow-up. After the first month, the cell-T immune response decreased within each group until month 6: KTR (M1 19.6%; M3 11.0%; M6 4.1%; p<0.001) and DP (M1 22.1%; M3 6.8%; M6 2.2%; p<0.001) but increased in both groups at month 12 (KTR 17,9%; DP 13,7%).
Conclusion: The sororreversion of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG was absent in both KTRs and DPs during 12 months of follow-up. Compared to DPs, KTRs had lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG titers, but similar neutralizing antibody activity and T-cell immune response at month 12.
#2021/13680-6, São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP).
[1] SARS-CoV-2
[2] COVID-19
[3] Kidney transplantation
[4] vaccination
[5] immune response
[6] SARS-CoV-2 Antibody
[7] Dialysis
[8] anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG
[9] neutralization antibody activity
[10] IFN-ɣ activity
