Impact of Gd-IgA1 predict of recurrent IgA nephropathy after kidney transplantation
Cheng-Hsu Chen1,2,3,4, Shuk-Man Ka5, Ann Chen6.
1Division of Nephrology, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan; 2Department of Post-Baccalaureate Medicine, College of Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan; 3Ph.D. Program in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, College of Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan; 4Department of Life Science, Tunghai University, Taichung, Taiwan; 5National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan; 6Hualien Tzu Chi Hospital, Hualien, Taiwan
Background: IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common glomerulonephritis in Asian, accounting for 26.8% of primary GN in Taiwan, and is also a leading cause of ESRD. In our previous report, recurrent IgAN is 39% in our kidney transplant recipients (KTR). The pathophysiology of IgAN recurrence is still limit, however, galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) and IgG anti-Gd-IgA1 antibodies might play a pivotal role in disease activity.
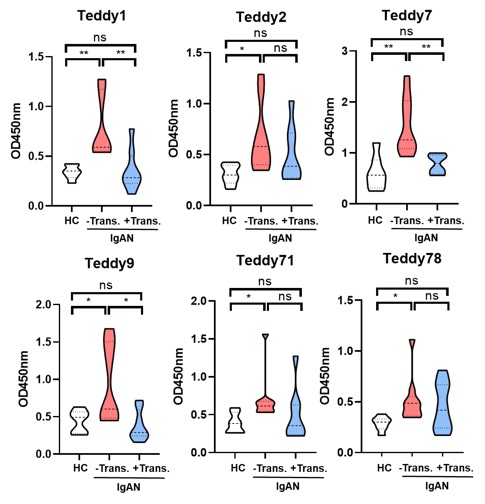
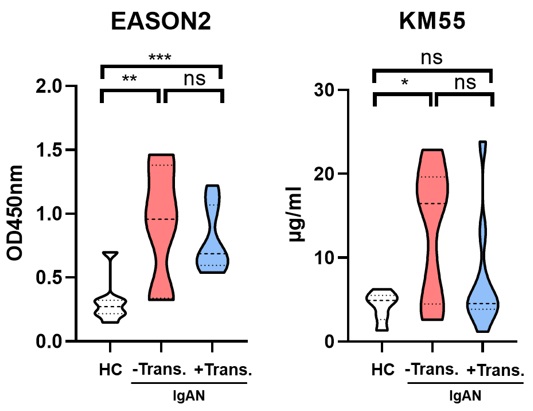
Materials and Methods: We recruited healthy normal subjects (n =7), biopsy-proven IgAN patients (n = 10) and recurrent IgAN KTR (n =9). Serum levels of Gd-IgA1 detected in all participants using human hybridoma-based IgG antibodies (Teddy1, Teddy 2, Teddy 7, Teddy 9, Teddy 71 and Teddy 78) and mouse Eason2 and KM55 antibodies.
Results: Each of them shows high discriminative rate in differentiating IgAN patients and healthy control subjects by doing ELISA-based analyses to determine serum Gd-IgA1 levels in all antibodies. The Gd-IgA1 levels in recurrent IgAN KTR were related lower than IgAN patients found in Teddy1, Teddy 7 and Teddy 9, and similar to healthy normal subjects, except in Eason2.
Conclusion: The long-term use of immunosuppressants might also suppress the Gd-IgA1 levels, however, the Eason2 antibody might be promising diagnostic reagents to detect the recurrent IgAN KTR. The further validation might be necessary for the clinical application.