Jeremias Elias Moreira, Argentina has been granted the TTS Basic and Translational Mentee-Mentor Award
Immunological effects of abdominal rectus fascia transplant in rats without immunosuppression, in the short and medium term
Jeremias Moreira1, Ivana Ivanoff2, Pedro Martín2, Verónica Milesi2, Pablo Stringa2,3, Constanza Arriola-Benitez1, Anastasios Giannou4, María Virginia Gentilini1, Martín Rumbo2, Gabriel E Gondolesi1,5.
1Instituto de Medicina Traslacional, Trasplante y Bioingeniería (IMETTyB), Universidad Favaloro-CONIC, CABA, Argentina; 2Instituto de Estudios Inmunológicos y Fisiopatológicos (IIFP), CONICET - Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Nacional de La Plata., La Plata, Argentina; 3Cátedra de Trasplante, Facultad de Ciencias Médicas, Universidad Nacional de La Plata., La Plata, Argentina; 4University Medical Center, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany; 5Servicio de Cirugía General, Trasplante Hepático, Pancreático e Intestinal., Universitario Fundación Favaloro, CABA, Argentina
Background: Currently, non-vascular Abdominal Rectus Fascia transplant (TxARF) is used in the clinic for primary closure of the abdominal wall. Since biopsies cannot be taken for study, its practice is limited to some patients on immunosuppressive treatment with abdominal organ transplantation. Our aim was to report the immune response and outcomes at short and medium term of experimental TxARF in rats.
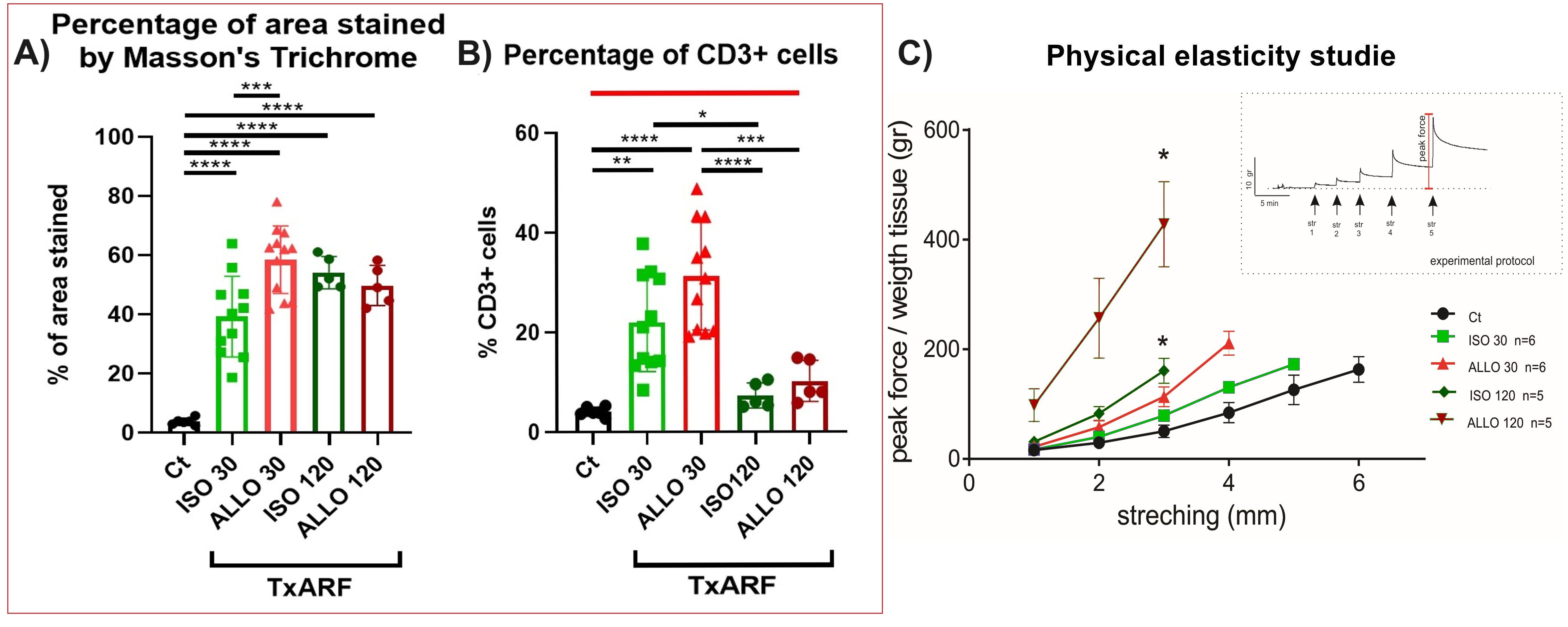
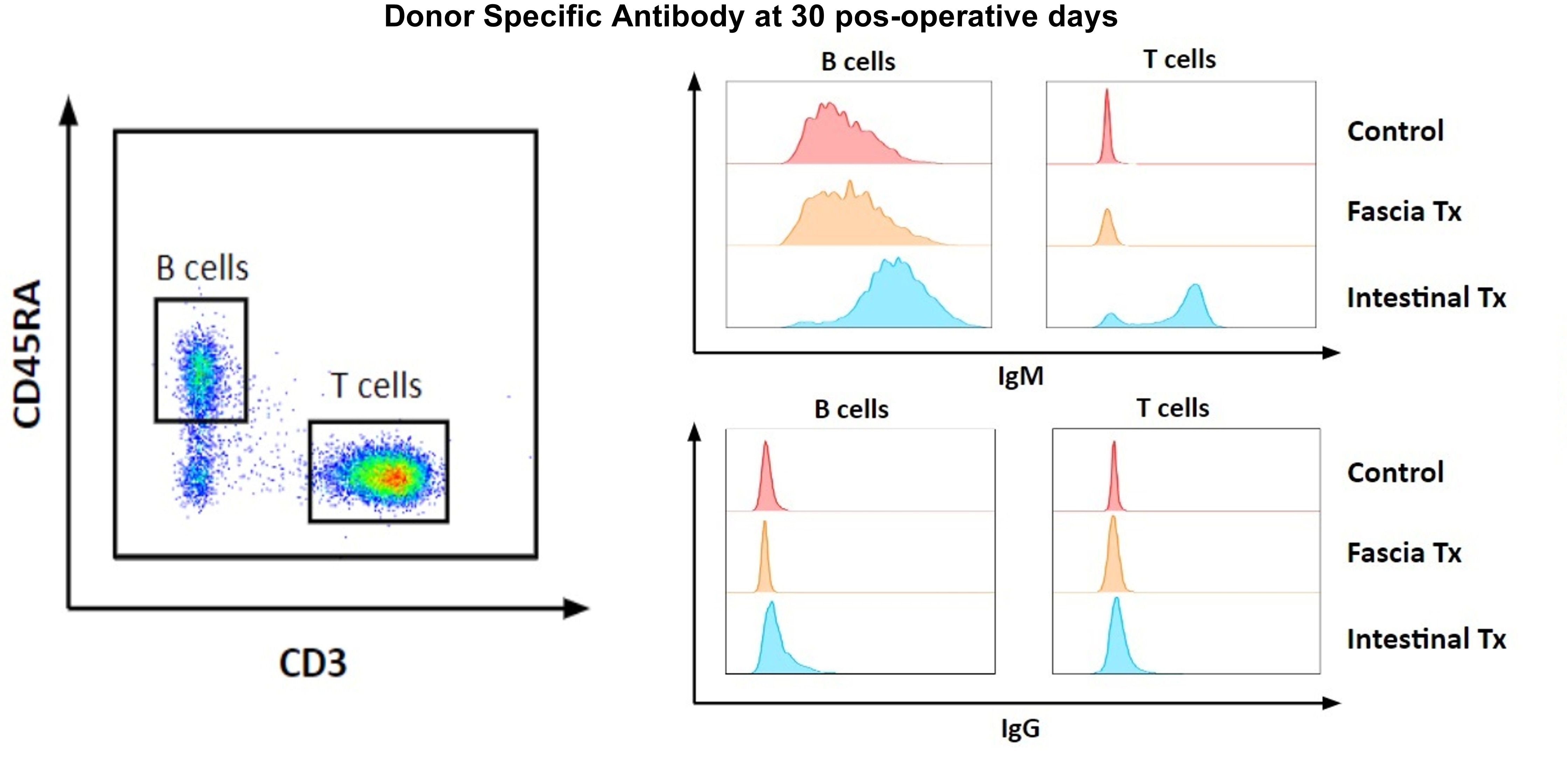
Materials and Methods: 34 TxARFs were performed in rats following our previous report, 32 were including; 16 Isogenic (ISO) and 16 Allogeneic (ALLO) TxARF without immunosuppression; 6 non-transplanted ARFs were taken as control group (Ct). PetScan of the graft was performed on some recipients at 30 and 120 pos-operative days (POD). Rats were sacrificed at 30 or 120 POD, fascia samples were taken for Masson's Trichrome, immunohistochemistry of CD3+ cells and mechanical properties studies. Tissue resistance was shown as the immediate force increase from a stretching stimulus (peak force, Fig.1), measured with a Letica Scientific Instruments force transducer. Flow cytometry was performed to determine the relative amounts of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and the turnover of hematopoietic cells in the graft using GFP+ rats as recipients. The presence of Donor Specific Antibody (DSA) in serum was evaluated (Fig.2). Statistical tests of Normality and One-way ANOVA tests were used for the analysis.
Results: The survival was 94.2%; 2 recipients were eviscerated and 3 ISO developed subcutaneous serum collection. None of the rats presented inflammatory activity by Petscan in the graft at 30 or 120 POD. The average percentage of collagen fibers was more than 10 times higher in all groups compared to Ct (p<0.0001). The average percentage of CD3+ cells at 30 POD was more than 5 times higher in ISO (21.92 + 9.77) and ALLO (31.24 + 10.81) compared to Ct (4.08 + 0.92). At 120 POD, neither the ISO (7.29 + 2.53) nor ALLO (10.20 + 4.15) had significant differences compared to Ct (Fig.1). The tissue resistance behavior (at 3mm of stretching), presents a tendency to increase compared to Ct, reaching statistical significance only in ALLO and ISO at 120 POD (Kruskal-Wallis One Way Analysis of Variance on Ranks p<0.05). At 30 POD, the proportions of CD4+ and CD8+ cells were similar in all groups. The origin of these cells was mainly from the recipient; 30% of the ALLO group were positive for DSA at 30 POD.
Conclusion: The increase in collagen fibers is compatible with a progressive fibrosis process that could be associated with the changes in mechanical tissue properties observed at 120 POD. However, the absence of inflammatory activity by PetScan, the low percentage of samples with DSA without immunosuppression and, the marked decrease in the percentage of CD3+ cells between 30 and 120 POD in ISO and ALLO, suggest a non-immunological origin of the fibrotic process. Although more studies are necessary, these results open the door to studying the potential usefulness of TxARF in non-transplantation.
[1] ARF
[2] non-vascular trasplant
[3] Experimental model
[4] Fascia
