Aberrant unsaturated fatty acid elongation induced GPNMB+CD206+ macrophages infiltration in steatotic grafts promotes HCC recurrence via mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation
Zheng Jian1, Jiang Liu1, Tao Ding1, Congwen Bian1, Albert Chi-Yan Chan1, Kwan Man1.
1Department of Surgery, School of Clinical Medicine, LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, Hong Kong
Prof. Kwan Man's group.
Background: GPNMB is a marker mainly found on macrophages with immunosuppressive function. Recent findings reveal that GPNMB+ CD206+ M2 macrophages are abundant in fatty liver, where they notably inhibit CD8+ T cell activity and antitumor immunity. In this study we aim to explore the relationship between unsaturated fatty acid elongation and the prevalence of GPNMB+ CD206+ macrophages in fatty grafts, and their impact on HCC recurrence post-liver transplantation (LT).
Methods: The expression of GPNMB and CD206 on macrophages were analyzed in liver graft samples by flow cytometry and multiplex IHC staining. The comprehensive analysis of fatty acid elongation enzymes in the fatty graft was performed both in clinical samples and rat liver transplantation model. The association of GPNMB and ELOVL1 was investigated in TP53KO/Myc HFMCD feeding spontaneous HCC mouse model. Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation activity was analyzed by seahorse.
Results: Clinically, GPNMB+CD206+ macrophages dominated in fatty liver grafts, correlating with heightened HCC recurrence risk (Figure 1A-C). RNA-seq analysis of human liver grafts and rat grafts revealed a surge in unsaturated fatty acid elongation activities, notably ELOVL1 (Figure 2A-B). The intragraft mRNA expression of GPNMB was positively correlated with ELOVL1 after LT (Figure 2C-D). Functionally, the liver specific ELOVL1 knockdown was established in the TP53KO/Myc HFMCD feeding spontaneous HCC mice model (Figure 3A), and ELOVL1 suppression mitigated tumor formation and reduced GPNMB+ CD206+ macrophages infiltration (Figure 3B). The C22:1 unsaturated fatty acid, a product of ELOVL1 enzymatic activity, exhibited significant alterations (Figure 4A). C22:1 promoted GPNMB and IL10 expression in macrophages (Figure 4B-C), yielding a M2-like polarization via mitochondrial FAO (Figure 4D).
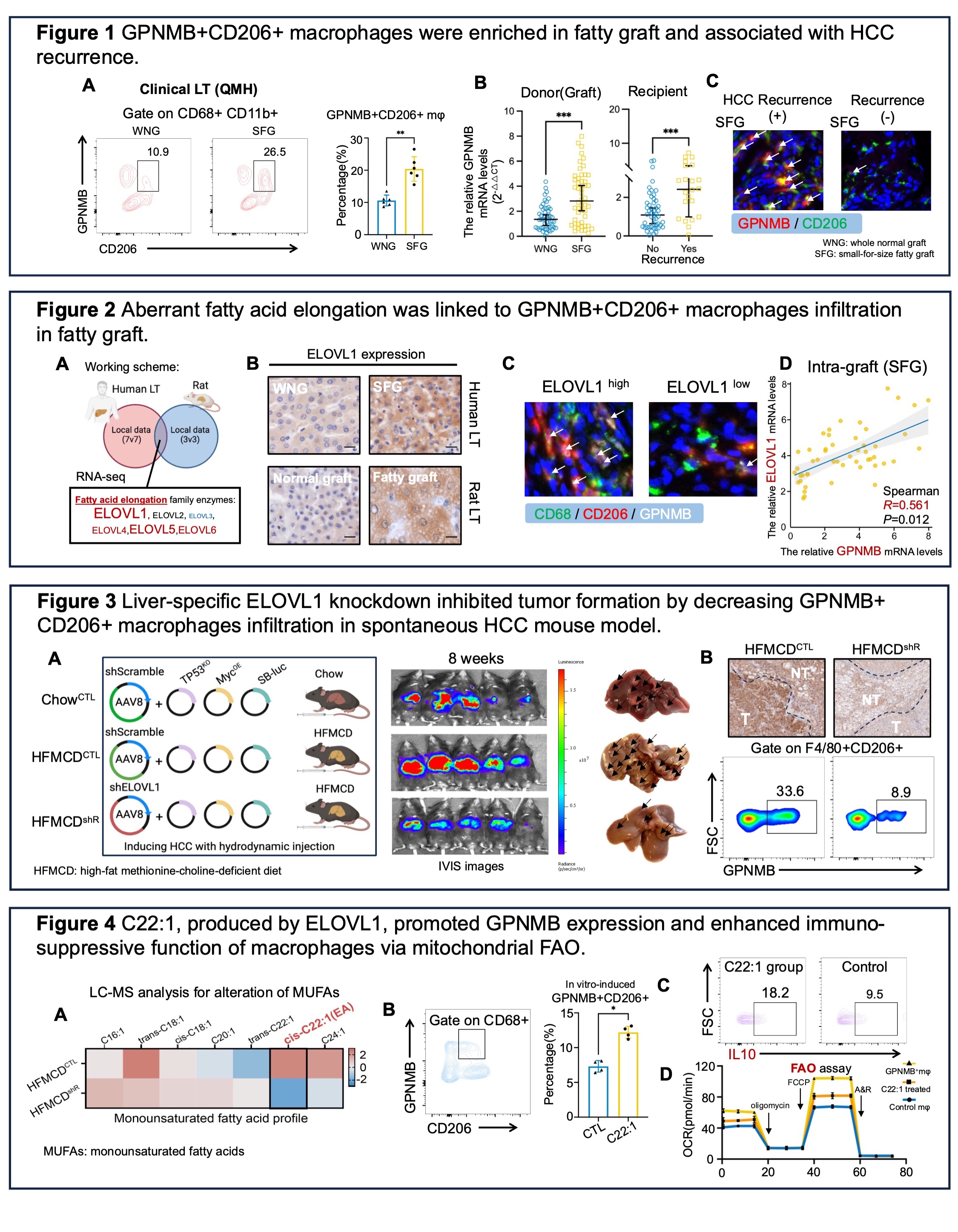
Conclusion: Dysregulated unsaturated fatty acid elongation enhanced GPNMB expression via mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in M2-like macrophages, and GPNMB+CD206+ macrophages promoted HCC recurrence after LT.
Our project are supported by TRS grant (T12-703/19-R)..
[1] Fatty graft
[2] Macrophages
[3] HCC recurrence
