Post-transplant dynamics of serum T50 and coronary artery calcium scores among kidney transplant recipients: The TransplantLines-CAC study
Amarens van der Vaart 1, Daan Kremer 1, Edward R. Smith 2,3, Rozemarijn Vliegenthart 4, Andreas Pasch 5,6, Jan-Luuk Hillebrands 7, Stephan J.L. Bakker 1, Martin H. de Borst1, Charlotte te Velde - Keyzer1.
1Department of Internal Medicine, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, Netherlands; 2Department of Nephrology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville Victoria,, Australia; 3Department of Medicine, University of Melbourne, Parkivlle Victoria, Australia; 4Department of Radiology, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, Netherlands; 5Calciscon, AG, Biel, Switzerland; 6Department of Physiology and Pathophysiology, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Linz, Austria; 7Department Pathology and Medical Biology, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, Netherlands
On behalf of TransplantLines Investigators.
Introduction: Kidney transplant recipients (KTR) remain at increased risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with the general population. This increased risk is fueled by an ongoing propensity to develop vascular calcifications, a phenomenon not fully elucidated. The serum T50 test quantifies the calciprotein particle transformation time, considered to reflect calcification propensity, and identifies KTRs with an increased mortality risk. This study aimed to investigate the association between serum T50 levels and computed tomography (CT)-based coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores at one year post-transplantation, with a follow-up assessment two years later.
Method: Participants of the TransplantLines-CAC study, a single-center cohort study in Groningen, The Netherlands, were screened between March 2018 and June 2021. Patients with established coronary artery disease or eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73m² were excluded. Demographic, lifestyle, and biochemical parameters were collected at baseline (12 months post-transplantation) and follow-up (36 months post-transplantation). Serum T50 levels were measured by sequential addition of calcium and phosphate solutions to serum. CAC scores were determined using low-dose, non-contrast CT with image reconstruction (3mm slice thickness) via the Agatston method.
Results: At baseline, 196 KTRs (mean age 54±15 years, 61% male, 70% with CAC) were included, with a median CAC score of 46 [0 – 470] Agatston units. Multivariable regression analysis revealed that mTOR inhibitor use, lower serum potassium or phosphate, and higher serum magnesium or transferrin were independently associated with higher serum T50. At baseline, serum T50 was associated with CAC score, independent of sex, age, and eGFR. However, baseline serum T50 was not significantly associated with CAC score at follow-up (Table 1A). In contrast, baseline CAC score significantly inversely correlated with serum T50 at follow-up, even after adjustment for sex, age, and correlates of serum T50 (Table 1B).
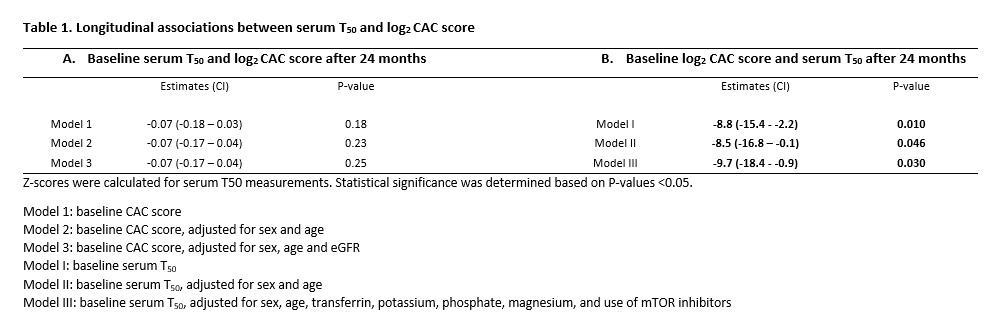
Conclusion: Although serum T50 at one year post-transplant was not associated with CAC score at follow-up, baseline CAC score was associated with serum T50 at follow-up. This suggests that the severity of vascular calcification influences serum T50 values, and that serum T50 may hold predictive value beyond vascular calcification. Understanding the dynamic interplay between vascular calcification and serum T50 levels may offer novel insights into cardiovascular risk stratification and guide personalized interventions after kidney transplantation.
Funding for this study was provided by the Dutch Kidney Foundation (Kolff Postdoc Startup Grant 17OKG02) and the University Medical Center Groningen (Mandema Stipend).
[1] coronary artery calcification
[2] kidney transplantation
[3] serum T50
[4] TransplantLines cohort
[5] vascular calcification
