Graft function stabilisation in chronic AMR: Can Tocilizumab be an option
Arpita Chaudhury(Lahiri)1, Abhishek Vashisth 1, Saugat Dasgupta 1, Sourav Sadhukhan1, Atanu Paul1, Koushik Bhjattacharya1, Sanjay Dasgupta1, Arunangshu Banerjee 1.
1Department of nephrology , IPGMER kOLKATA , NBMCH, West bengal, kolkata , India
Introduction: Long term transplant outcome remains dismal, particularly in low-risk populations like living donor recipients, there had been no improvement in last 2 decades. Chronic antibody mediated rejection(CAMR), the most important contributory cause has few effective treatment options. One emerging option is Tocilizumab, IL6 receptor inhibitor, for modulation of inflammation and humoral immunity , benefits mediated by stabilizing graft function, reducing dn-DSA load, decreasing anti-HLA IgG Total and IgG3 load, and improving KT histology pre vs post intervention. We had intervention with tocilizumab( Intervention TCZ arm, prospective cohort) ) on top of current standard of care therapy i.e. IVIg +/-Rituxmab +/-Plasmaphesis (SOC, historical cohort) and looked for any additional benefit in TCZ arm.
Methods: We identified 30 patients diagnosed cABMR from 2017 to June 2022 in IPGMER, Kolkata or elsewhere who received treatment with us. All received IVIG at dose 2gm/kg and rituximab with or without plasmapheresis. Tocilizumab intervention given in 10 patients who gave consent with dose of 8 mg/kg single dose every month for next 2 years, with prior negative screening for infections. Most patients were low risk living donor transplants received IL2 Blocker( high risk:4/ 10 in TCZ group and 16/ 20 in SOC arm, received ATG induction). All patients were on standard 3 drug IS with appropriate Tac level target achieved . We could not frequently measure dn-DSA (outsourced) .Standard CKD retardation regime was followed for all. As an outcome measure for percentage proteinuria improvement ( surrogate marker of renal progression, CV mortality)and mean change of serum creatinine ( graft function stabilization) along with graft and patient survival in both arms.
Findings: Mean age of the recipients, gender distribution, induction and maintenance immune suppression were not different in SOC vs TCZ arm. SOC arm at 15 mo follow up, 8/20 patients are HD free,6 patients died ( infections and CV mortality, 3 each) 2 became HD dependent before death,with optimized CKD retardation mean graft and patient survival 28.3 months and 24.7 months respectively. In TCZ group 2 patients were initiated on HD, but rest are HD free, no infection related death. Baseline vs M15 proteinuria in TOC vs STD arm is shown in fig 1a and Baseline vs M15 serum creatinine is shown in in Fig 1b.Median percent change in serum creatinine in TOC arm was increased by 43% (20.55%,73.06%) and in SOC arm by 88.76% (70.26%,142.86%) p>0.005. Mean percent decrease of proteinuria in TOC arm was -19.215% (SD- 36.9) vs mean percent change in proteinuria was 16.22% (SD- 27.92) p=0.006.
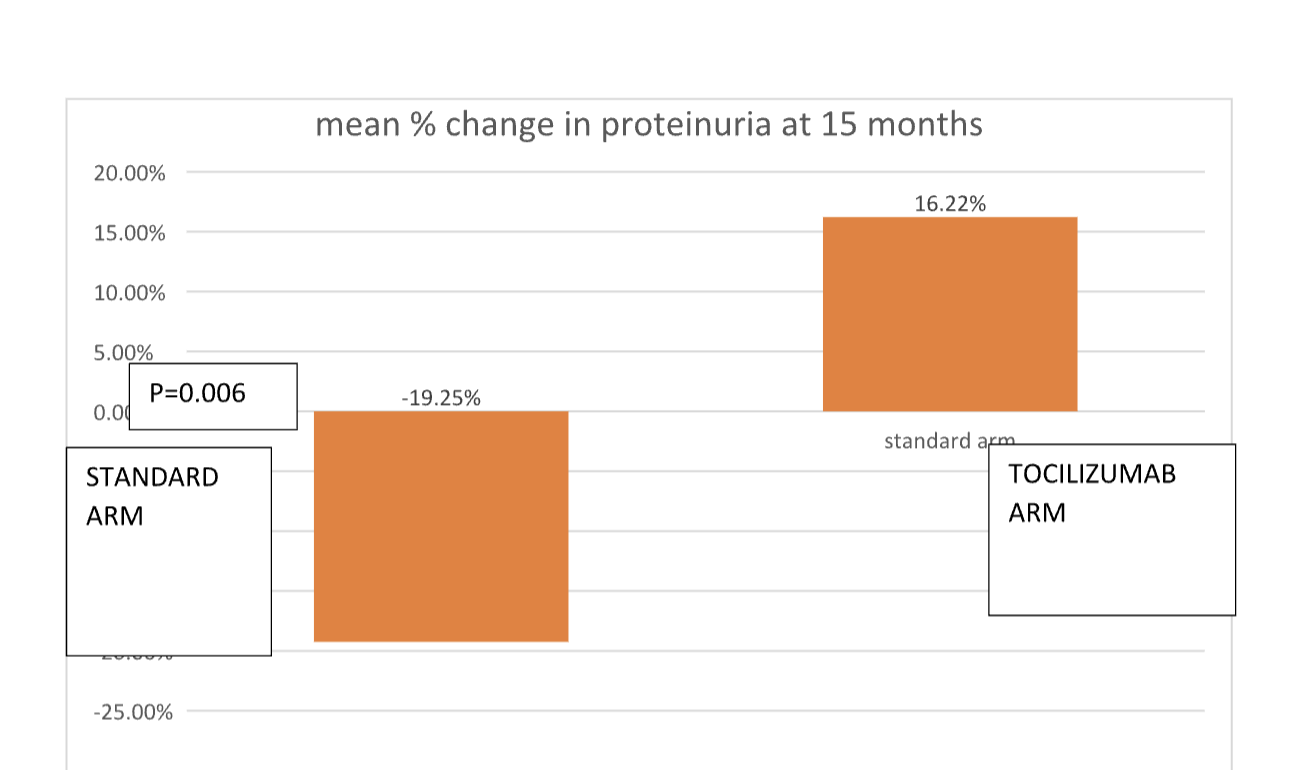
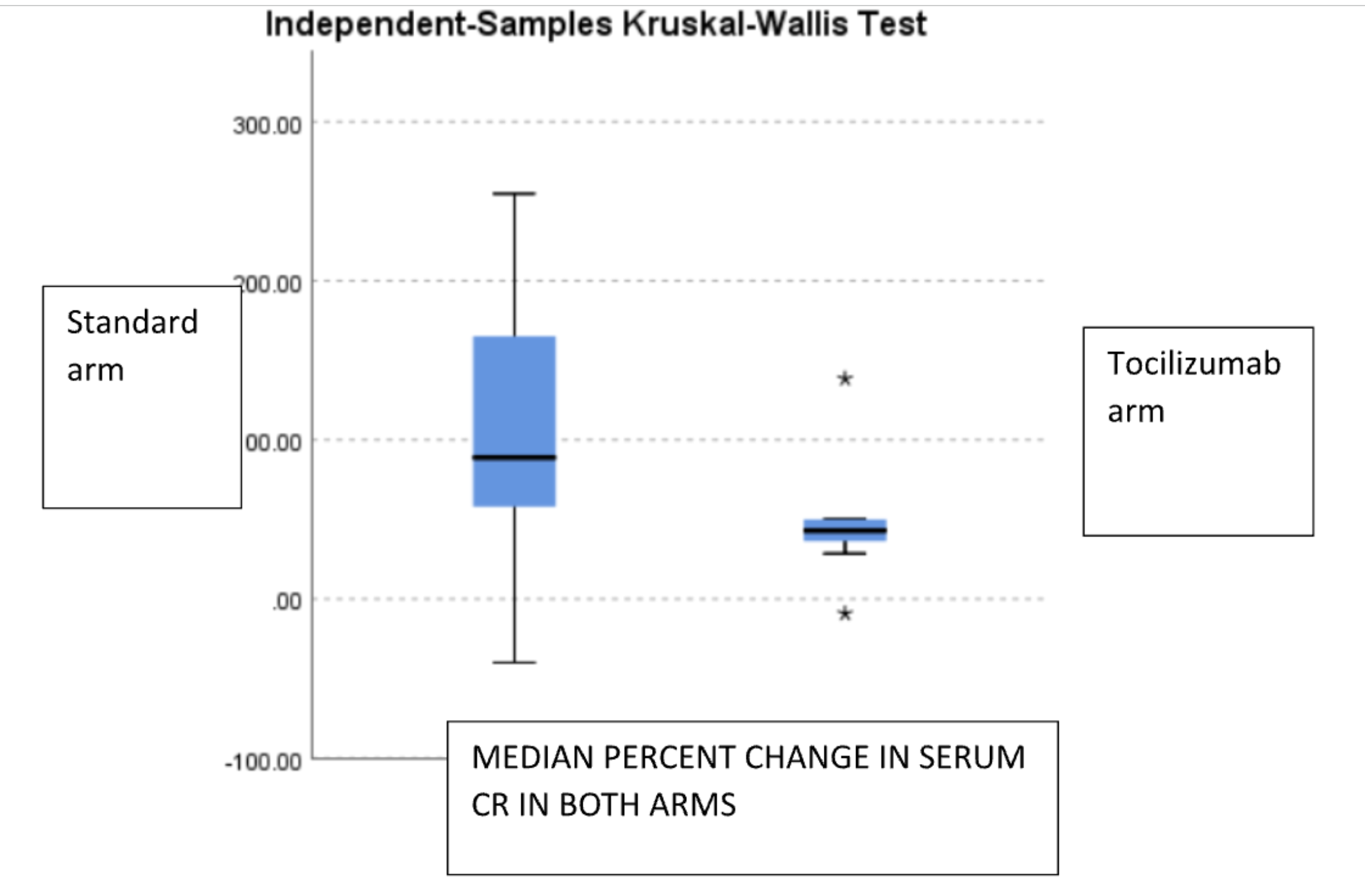
Conclusion: Tocilizumab may stabilize graft function better on top of standard of care The proteinuria reduction may be explained by reduction of inflammation in IFTA region ,confirmation needs a repeat biopsy at end of proposed term at 2 years.
