Comparison of anti-human T-Lymphocyte immunoglobulin (r-ATLG - Grafalon) vs anti-thymocyte globulin (r-ATG - Thymoglobulin) in kidney transplant: A 5-year follow-up study
Vijay Kumar Sinha1.
1Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation , Jaypee Hospital, Noida, India
Introduction: T cell depletion agents, Thymoglobulin (ATG) and Grafalon (ATLG), are commonly employed as induction agents in kidney transplantation. This study aims to assess the short- and long-term outcomes of kidney transplants at our centre focusing on the use of these agents.
Method: This retrospective study analysed data from kidney transplant patients at a tertiary care hospital in INDIA, between 2017 and 2024. Of the 581 patients included, 375 received Thymoglobulin and 206 received Grafalon as induction therapy. All patients were maintained on standard triple immunosuppressive therapy. Follow-up included monitoring for graft rejections, infections, de novo disease, and overall graft survival.
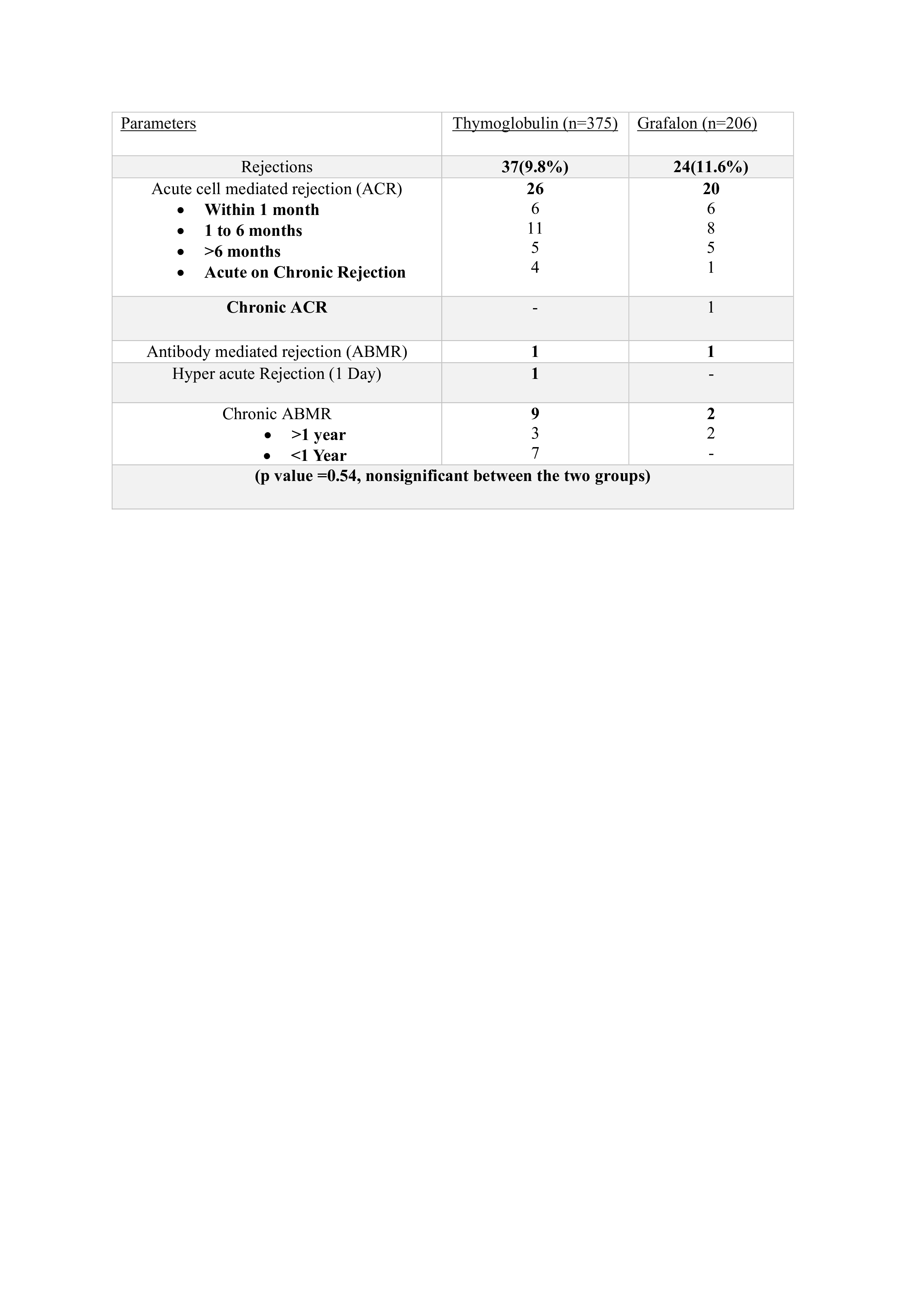
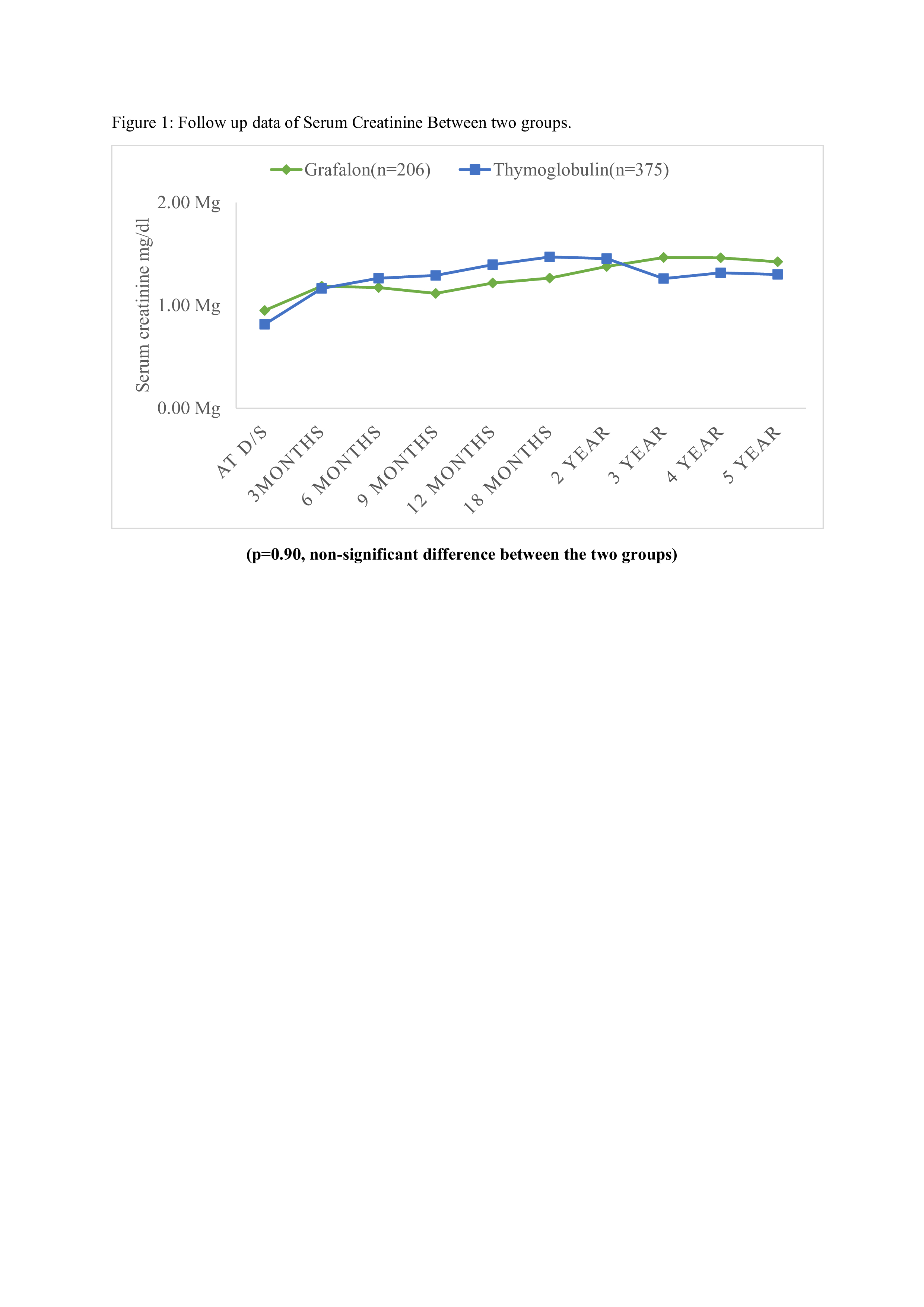
Results: The average duration of follow-up spanned 60 months. The mean doses of Grafalon and Thymoglobulin were 5.4±1.4 mg/kg and 2.37±1.2 mg/kg, respectively. Baseline characteristics were consistent across both groups. Figure 1 depicts the serum creatinine levels at discharge and during subsequent follow-up intervals. Table 1 provides a comprehensive overview of rejection outcomes over a 5-year follow-up period, distinguishing between the Thymoglobulin and Grafalon cohorts. Notably, there was a higher incidence of de novo diseases observed within the Thymoglobulin cohort (12 cases, 3.2%) compared to the Grafalon cohort (3 cases, 1.4%). However, the incidence of infections exhibited comparability between the two groups.
Conclusion: Both the short-term and long-term outcomes of kidney transplant recipients receiving Thymoglobulin or Grafalon as induction therapy were similar in terms of graft rejection incidence. However, Thymoglobulin was associated with a higher occurrence of de novo diseases (this may be an incidental finding or due to some unexplained reasons).
[1] Induction Therapy, Grafalon, Thymoglobulin, Acute Cellular Rejection and Long term Data
