Dynamics of organ transplantation in a state in northern india: unraveling timelines in government & private healthcare system
Akanksha Chowdhary1, Rajesh Harshvardhan2, Vaibhav Shriya2, Saurabh Singh1.
1Trauma Centre, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University , Varanasi, India; 2Department of Hospital Administration, Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
Introduction: Organ transplantation is the surgical procedure of replacing a failing or damaged organ in the human body with a healthy organ from a donor, aimed at restoring or improving the recipient's health and quality of life. In the context of Uttar Pradesh (U. P.), India, organ transplantation has gained prominence as a vital therapeutic option.
Aim & Objectives: The objective of the study is to assess the timeline of organ transplantation among the Healthcare Organization of U. P.
Materials & Methods: An observational survey was conducted on data from 52 Transplant Centers, registered under State Organ & Tissue Transplant Organization – Uttar Pradesh (SOTTO – U. P.)
Study Duration: December, 2020 – April, 2023
Data Collection Tool: Standard Data Reporting Format for Organ Transplantation, as provided by NOTTO
Data Analysis: Data was entered into MS Office Excel 2021 & statistically analyzed with SPSS version 23.
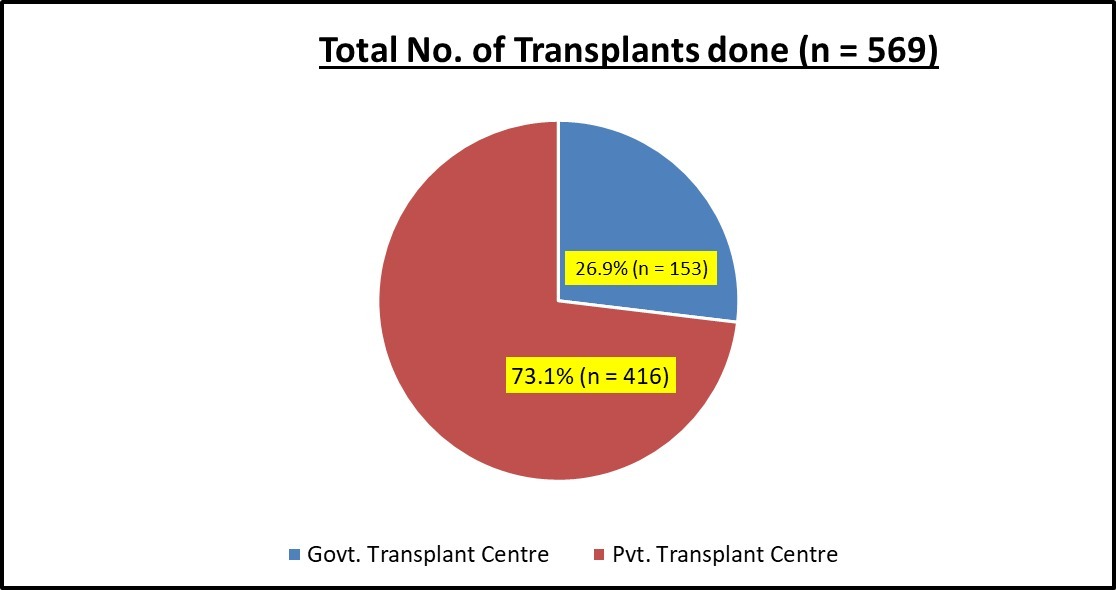
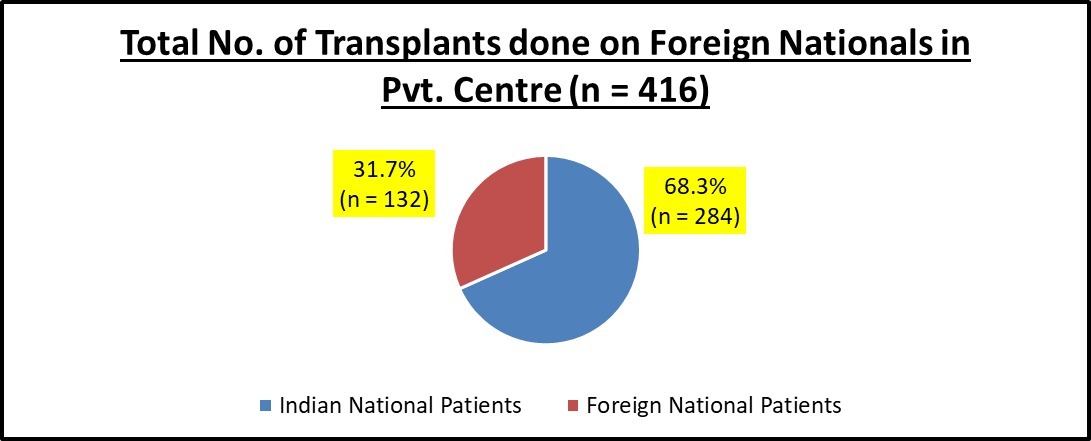
Results: Data from 569 transplants was analyzed & 73.1% (n = 416) of the transplants were performed in Private transplant facilities. The median age of organ donor & recipient in both govt. & private Transplant Centre was 35 & 37 years respectively. Majority donors were females & were related to recipient (n = 357, p= <0.001). This correlation was insignificant in foreign nationals. There was negative correlation between the age of donor & recipient (p= <0.001). It was further noted that all transplant performed in Government Transplant centres were of Indian nationals (n=153), whereas in private centres, 31.70% (n = 132) patients were foreign nationals
There is a significant difference (p < 0.001) in the median duration of Organ Transplant between Govt. (142 days) & Private Transplant (12 days) centers. Renal transplantation, at 78.2 % (n = 445), was majorly performed, with median duration of 29 days. The median duration for liver transplant in both type of centers is 3 days & 5 days, respectively (p= 0.416).
Only 1.23% (n = 7; n = 1 in Liver & n = 6 in Kidney) transplants were by Deceased Donor Organ Transplant (DDOT) program.
Conclusion: Comprehensive reforms are necessary to minimize discrepancies and ensure equitable access to organ transplants for all patients, regardless of hospital type, within Uttar Pradesh.
Recommendations:
[1] Organ Transplantation
[2] Organ Donation
[3] Northern India
