A cross sectional study of the medium term outcomes in living donor renal transplant recipients developing ATN in the immediate post transplant period
Alok Kumar1, Sharmila Thukral1, Deepak Ray1.
1Nephrology, NH Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, Kolkata, India
Introduction: Acute tubular necrosis(ATN) is commonly observed in renal transplant recipients (RTRs) in the immediate post transplant period. It occurs is 20-50% in recipients of deceased donor kidneys and 4-10% in living donor kidneys. There are very few studies about the outcome of the RTRs developing ATN in living donor RTRs. This study was done to study the medium term outcomes - graft and patient survival, incidence of rejections, infections and delayed graft function(DGF) in RTRs developing biopsy proven ATN in the immediate post transplant period.
Methods: Study was conducted at a tertiary care center in Eastern India.RTRs who developed ATN (biopsy proven) from January 2013 to December 2017 were included in the study. Data of these patients & respective donors was collected. Minimum period of follow-up was 5 years post-transplant.Cold and warm ischaemia time, incidence of surgical complications, acute rejections, infections, graft survival , patient survival were noted. RTRs were followed up regularly in post transplant period with relevant investigations .The cohort was divided in two groups–DGF group and non-DGF group. A comparative analysis was done between the two groups. Data was analysed using SPSS version 26.
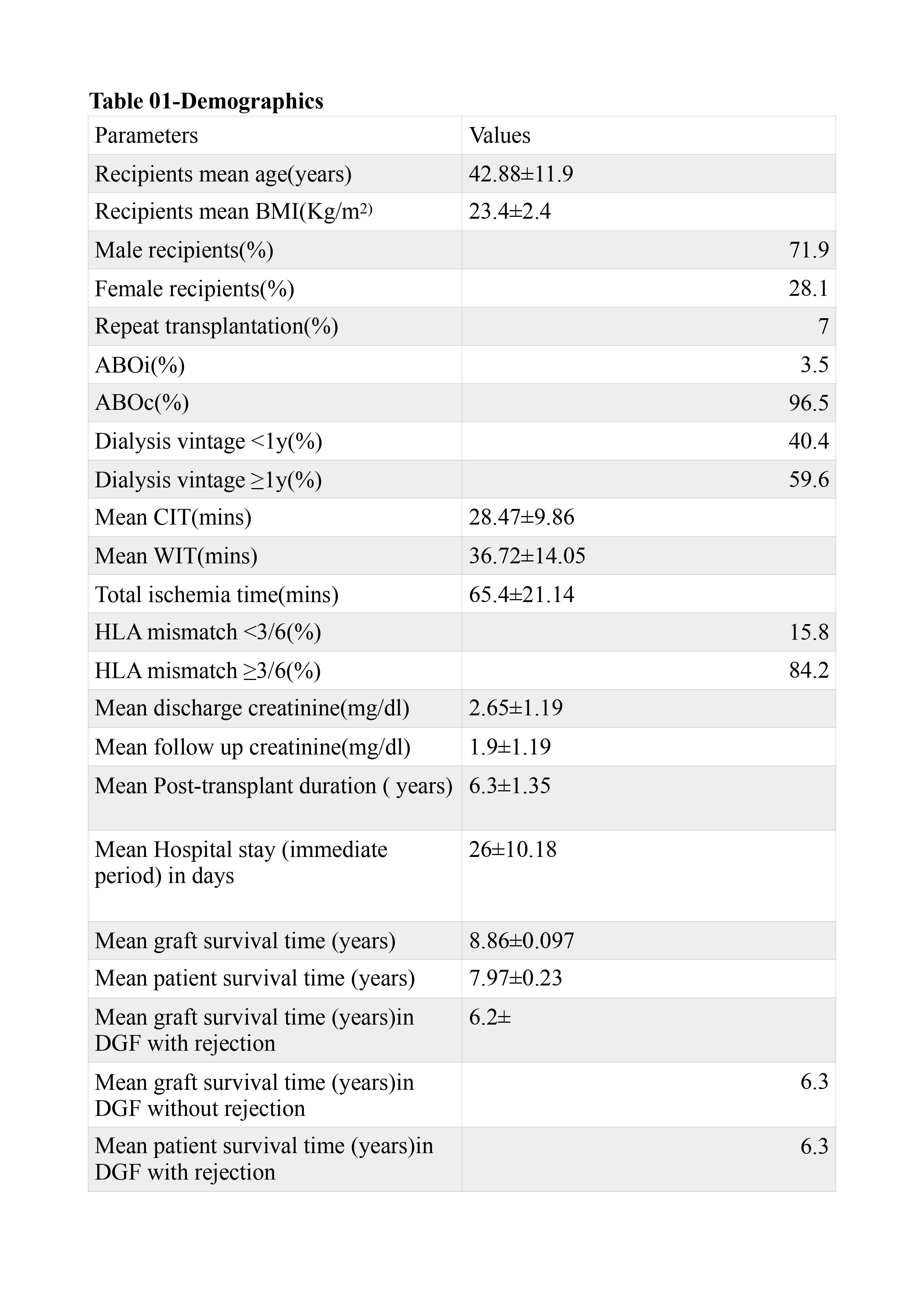
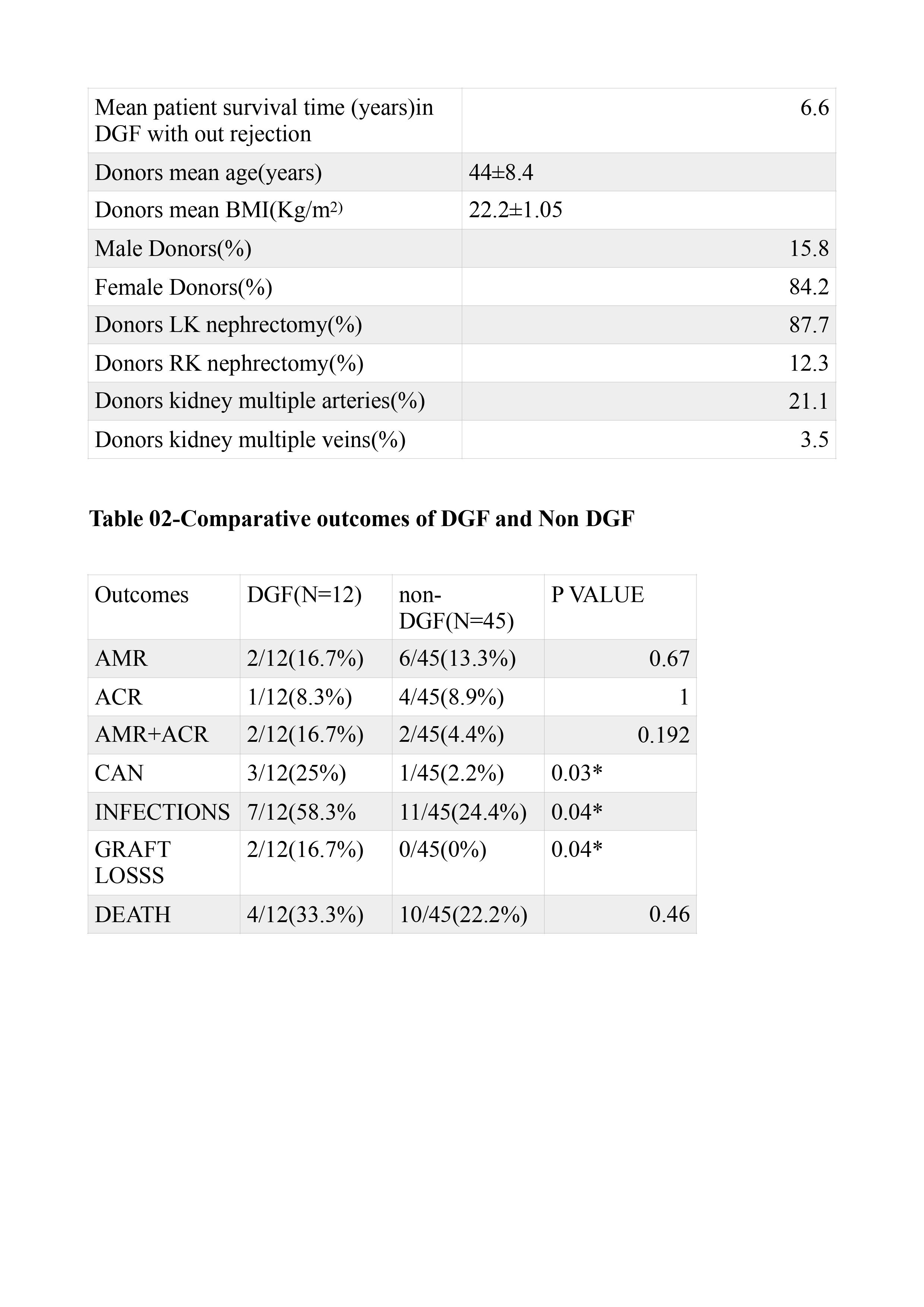
Results: 57 RTRs developing ATN were included . Male /female ratio was 2.56 :1.Mean age of recipients was 42.88 ±11.9 years. Mean warm ischemia time was 36.72 ±4.05 minutes, cold ischemia time was 28.47±9.86 mins and total ischemia time was 65.40 ±21.14 mins. Mean duration of hospital stay in the immediate post-transplant period was 25.82 ±10.2 days. Mean duration of follow up was 6 ±1.8 years. 84% of donors were female and mean age of donors was 43±8.5 years.12.3% of donors underwent right kidney nephrectomy and 87.7% underwent left kidney nephrectomy. 21.1% of donor kidneys had multiple arteries. Surgical site bleeding was seen in 29(50.9%) .17(29.8%)of recipients had acute rejections -12 in DGF and 5 in non-DGF group. 4(7%) developed chronic allograft nephropathy (CAN) – 3 in DGF and one in non-DGF group.18 (31.6%) developed infections –11 in DGF and 7 in non-DGF group. Patient survival was 75.4% at follow up and mean survival time was 7.98 years. Graft survival was 96.5% and mean graft survival time 8.86 years.12 patients (21.05%) developed DGF. Patient survival in DGF and non DGF group was 67% and 78% respectively.Graft survival in DGF and nonDGF group was 84% and 100% respectively (statistically significant).2 out of 12 DGF patients lost their graft. Significant association of DGF with CAN , infections and graft loss.
Conclusion: DGF secondary to ATN in the immediate post transplant period adversely affects the graft outcomes in medium term. The incidence of infections, CAN and graft loss is significantly higher in DGF group compared to non-DGF group.
[1] ATN
[2] DGF
[3] Graft Survival
[4] Patient Survival
[5] Living donor renal allograft recipients
